

Where, ℓ = azimuthal quantum number of the subshellįor s subshell, ℓ = 0 For p subshell, ℓ = 1 For d subshell, ℓ = 2 For f subshell, ℓ = 3 We can calculate the number of orbitals in each subshell using the formula: 2ℓ + 1
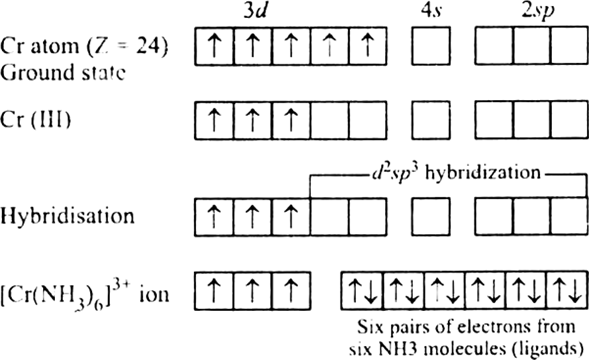
#Chromium orbital diagram how to
Learn how to find: Vanadium Electron Configuration The electron configuration of vanadium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 3. #2 Write Electron Configuration of Vanadium
Since the atomic number of vanadium is 23, the total electrons of vanadium are 23.

There is no hard and fast rule for this, but that is an explanation that correlates with experimental data.The atomic number of vanadium represents the total number of electrons of vanadium. Thus, electron pairing is favorable enough for Tungsten. The more the electron distribution is spread out, the less electron-pair repulsion there is, and thus the lower #Pi_c# is. However, Tungsten's #5d# and #6s# orbitals being larger than the #3d# and #4s# orbitals (respectively) spreads out the electron density enough that the pairing energy ( #Pi = Pi_c + Pi_e#) is small enough.

#Chromium orbital diagram series
One explanation for Chromium, then, is that: New criteria for assigning the spectra of these complexes are introduced and the data pro- cessed to yield a series of crystal field and molecular orbital. The former is stabilizing and the latter is destabilizing, as shown below (suppose configuration 2 is at pairing energy #Pi = 0#): These combine to produce an overall pairing energy #Pi = Pi_c + Pi_e#.The coulombic repulsion energy #Pi_c# (a destabilizing factor that is inversely proportional to the number of electron pairs).The exchange energy #Pi_e# (a stabilizing quantum mechanical factor that is directly proportional to the number of pairs of electrons in the same subshell or very close-energy subshells with parallel spins).To explain Chromium's electron configuration, we could introduce: Unfortunately, there is no easy way to explain these deviations in the ideal order for each element. Interestingly enough, Tungsten is more stable with an electron arrangement of #4f^14 5d^4 6s^2#.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
